
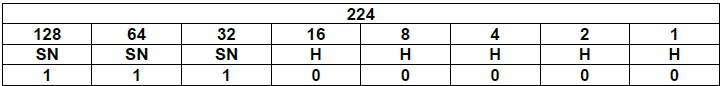
The first column shows how many bits are borrowed from the host portion of the address for subnetting. There are three tables, one for each class of addresses. The following tables show all possible ways a major network can be subnetted, and, in each case, how many effective subnets and hosts are possible.

A subnet mask defines which portion of the address is used to identify the network and which denotes the hosts. This is done by borrowing bits from the host portion of the IP address, enabling more efficient use of the network address. Subnetting is the concept of dividing the network into smaller portions called subnets. Multicast IP addresses have their first octets in the range 224 to 239.Ĭlass E-Reserved for future use and includes the range of addresses with a first octet from 240 to 255. The first octet range of 192 to 223 is a Class C address.Ĭlass D-Used for multicast. Any address whose first octet is in the range 128 to 191 is a Class B address.Ĭlass C-The first three octets denote the network address, and the last octet is the host portion. Note that 0 is reserved as a part of the default address, and 127 is reserved for internal loopback testing.Ĭlass B-The first two octets denote the network address, and the last two octets are the host portion. Any IP address whose first octet is between 1 and 126 is a Class A address. The following are the classes of IP addresses.Ĭlass A-The first octet denotes the network address, and the last three octets are the host portion. Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
#Cisco subnet mask table software#
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions. There are no specific requirements for this document. For more information on IP addressing, refer to IP Addressing and Subnetting for New Users. Each of the octets can be represented in a decimal format, separated by decimal points. The IP address is generally represented using the dotted-decimal notation, where 32 bits are divided into four octets. The host (or node) address is used to identify a particular device attached to the network. The network address is used to identify the network and is common to all the devices attached to the network. IP routers do not forward network broadcast packets.An IP address is 32 bits long and made up of two components, a network portion and a host portion. IP broadcast addresses can be used only as the destination IP address. It is used by certain firewalls and routers like Cisco for access control listīroadcast: The broadcast of a network is a reserved address to send a message to all hosts in the subnet. Wildcard: The wildcard is the inverse of the subnet mask. For a /31 subnet with only two possible address, the number of usable addresses would be zero. Generally, within a subnet, two host addresses - all-zeros and one all-ones are reserved as network address and broadcast, respectively. Without CIDR, the routing table would become quite large, as every network needs an own entry. Consider this example, where a router needs to distribute traffic for eight separate networks through the gateway 192.168.1.1: ip route 192.168.2.0/27 192.168.1.1 Simply spoken, CIDR using address aggregation can be used to address multiple networks with one single routing entry. Another problem with a classful setup is, that the bandwidth usage is quite high when routers exchange their routing information. But also the performance was compromised, since large tables need to be looked up without a more dynamic IP interval mechanism, like CIDR imposes. The memory usage of classful routing is enormous, which results in unreasonable expensive hadware. What is CIDR?ĬIDR or Classless Inter Domain Routing was developed to reduce the increasing size of routing tables of large routers, which was quite hard with classful routing.

Please note: IP addresses can be cut off, if the remaining octets are just zero. 192.168.0.1: Simple Address in standard class.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
